
What are RAM and ROM
RAM and ROM are nothing but a type of memory that serves different purposes, Before understanding what are RAM and ROM we have to first know about Memory.
What is Memory?

Before understanding, RAM and ROM you have to first know about Memory.
Data and instructions are stored in memory. Computer memory is the area where instructions for processing data and data that have to be processed are kept.
A computer system’s memory is its most crucial component since, without it, a computer cannot carry out basic operations.
Types of Memory

Computer memory has two fundamental types: RAM and ROM are the main memory. Read-Only Memory (ROM) is the primary non-volatile memory, whereas Random Access Memory (RAM) is the major volatile memory.
Many individuals frequently mix this two together and get confused. Follow this blog to learn the distinction between RAM and ROM and to have a strong understanding of it.
What is RAM?
Random access memory is another name for RAM. Users may read and write data operations thanks to it. It is used to store the information and programs that the CPU uses in real/present time.
The RAM’s data may be read, written to, and destroyed several times. RAM is referred to as a temporal memory since the data it keeps is only accessible while the power is on. It is only a piece of computer hardware that houses the computer’s working short-term memory.
Types of RAM:
- SRAM—statistic random access memory—stores a bit of data based on the state of a memory cell with six transistors. There are four to six transistors in it. In comparison to DRAM, an SRAM cell requires more transistors to construct, which increases the cost, lowers the density, and increases power consumption when reading or writing data.
- DRAM – Dynamic random access memory is regarded as the primary memory of the computer. A data bit is disturbed in the capacitor of a DRAM memory cell, which consists of a transistor and a capacitor inside of an integrated circuit. The capacitor has two possible states: charged and discharged. Because transistors always leak a tiny amount, causing capacitors to discharge and erasing the data they contain, DRAM must be recharged frequently in order to maintain data retention.
Static random-access memory (SRAM) and dynamic random-access memory are the two primary varieties of volatile random-access memory (DRAM). IBM debuted the SP95 SRAM chip for their System/360 Model 95 computer in 1965, while Toshiba employed DRAM memory cells for its Toscal BC-1411 electronic calculator.
Both of these devices were based on bipolar transistors.
The development of commercial MOS memory, based on MOS transistors, in the late 1960s, served as the foundation for all subsequent commercial semiconductor memory. The Intel 1103, the first DRAM IC chip for use in consumer electronics, was released in October 1970. The Samsung KM48SL2000 chip introduced synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) a year later in 1992.
What is ROM?
A form of non-volatile memory used in computers is termed read-only memory (ROM). Because the information recorded in ROM is permanent, it is a non-volatile memory, meaning it keeps its contents even when the power is turned off. Even yet, there are several extremely particular techniques that may be used to rewrite the data that is stored in ROM.
Non-volatile memory is another name for this kind of memory. Before the CPU may access the contents of these memories, they must first be transferred to the random access memory.
Types of ROM:
- PROM– a variant of ROM in which the data is written after the memory chip has been made. PROMs are programmable read-only memories. This contains permanent, unchangeable data. They serve as persistent data storage in electronic gadgets. The data is programmed into it after the manufacturing process, which is its primary feature.
- EPROM– Erasable programmable read-only memory The one type of ROM that can be wiped and reused is memory. By shining intense UV light on this non-volatile memory chip, the data may be removed.
- EEPROM– Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory, or EEPROM, is a form of ROM that keeps all of the data it has recorded even after the power is turned off. Field electron emission may be used to electrically erase and rewrite the data in this memory chip, bypassing the requirement to unplug the EEPROM from the device while rewriting the data.
- MROM– Masked read-only memory—is a sort of ROM where information is recorded when a memory chip is being manufactured.
IBM stored the microcode for the first two System/370 models (370/155 and 370/165) as well as the smaller System/360 models, the 360/85, utilizing capacitor read-only storage (CROS) and transformer read-only storage (TROS). A writeable control store (WCS) was also available on select versions for further diagnostic and emulation functionality. The core rope memory employed by the Apollo Guidance Computer was programmed by weaving wires through magnetic cores.
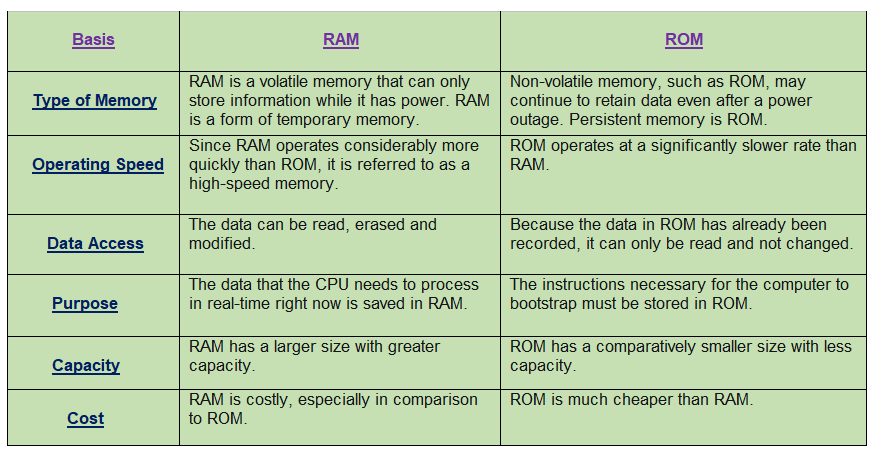
Key Difference between RAM and ROM














1 Comment
[…] Mediatek Processor Mobile Phones till the first half of 2022 What are RAM and ROM Is it ok to leave a smartwatch charging overnight? what are the pros and cons of rooting […]